PID thermostat with LogicMachine
Example: PID thermostat with LM
PID function
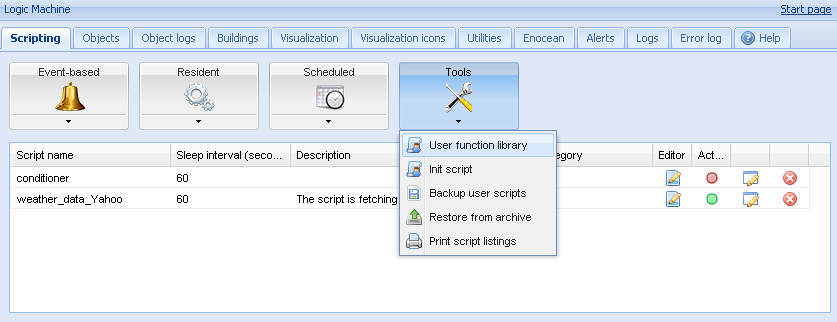
There is a PID function already added by default in Logic Machine -> Scripts -> Tools menu.
- PID = {
- -- default params
- defaults = {
- -- invert algorithm, used for cooling
- inverted = false,
- -- minimum output value
- min = 0,
- -- maximum output value
- max = 100,
- -- proportional gain
- kp = 1,
- -- integral gain
- ki = 1,
- -- derivative gain
- kd = 1,
- }
- }
-
- -- PID init, returns new PID object
- function PID:init(params)
- local n = setmetatable({}, { __index = PID })
- local k, v
-
- -- set user parameters
- n.params = params
-
- -- copy parameters that are set by user
- for k, v in pairs(PID.defaults) do
- if n.params[ k ] == nil then
- n.params[ k ] = v
- end
- end
-
- -- reverse gains in inverted mode
- if n.params.inverted then
- n.params.kp = -n.params.kp
- n.params.ki = -n.params.ki
- n.params.kd = -n.params.kd
- end
-
- return n
- end
-
- -- resets algorithm on init or a switch back from manual mode
- function PID:reset()
- -- previous value
- self.previous = grp.getvalue(self.params.current)
- -- reset iterm
- self.iterm = 0
- -- last running time
- self.lasttime = os.time()
-
- -- clamp iterm
- self:clampiterm()
- end
-
- -- clamps iterm value
- function PID:clampiterm()
- self.iterm = math.max(self.iterm, self.params.min)
- self.iterm = math.min(self.iterm, self.params.max)
- end
-
- -- clamp and set new output value
- function PID:setoutput()
- local t, object, value
-
- self.output = math.max(self.output, self.params.min)
- self.output = math.min(self.output, self.params.max)
-
- value = math.floor(self.output)
- local t = type(self.params.output)
-
- -- write to output if object is set
- if t == 'string' or t == 'table' then
- if t == 'string' then
- self.params.output = { self.params.output }
- end
-
- for _, output in ipairs(self.params.output) do
- grp.write(output, value, dt.scale)
- end
- end
- end
-
- -- algorithm step, returns nil when disabled or no action is required, output value otherwise
- function PID:run()
- local result
-
- -- get manual mode status
- local manual = self.params.manual and grp.getvalue(self.params.manual) or false
-
- -- in manual mode, do nothing
- if manual then
- self.running = false
- -- not in manual, check if reset is required after switching on
- elseif not self.running then
- self:reset()
- self.running = true
- end
-
- -- compute new value if not in manual mode
- if self.running then
- -- get time between previous and current call
- local now = os.time()
- self.deltatime = now - self.lasttime
- self.lasttime = now
-
- -- run if previous call was at least 1 second ago
- if self.deltatime > 0 then
- result = self:compute()
- end
- end
-
- return result
- end
-
- -- computes new output value
- function PID:compute()
- local current, setpoint, deltasc, deltain, output
-
- -- get input values
- current = grp.getvalue(self.params.current)
- setpoint = grp.getvalue(self.params.setpoint)
-
- -- delta between setpoint and current
- deltasc = setpoint - current
-
- -- calculate new iterm
- self.iterm = self.iterm + self.params.ki * self.deltatime * deltasc
- self:clampiterm()
-
- -- delta between current and previous value
- deltain = current - self.previous
-
- -- calculate output value
- self.output = self.params.kp * deltasc + self.iterm
- self.output = self.output - self.params.kd / self.deltatime * deltain
-
- -- write to output
- self:setoutput()
-
- -- save previous value
- self.previous = current
-
- return self.output
- end
Usage
- p = PID:init(parameters)
- p:run()
Parameters
Mandatory:
- current – (object address or name) current temperature value (2 byte float or any numeric value)
- setpoint – (object address or name) temperature set point value (2 byte float or any numeric value)
Optional:
- manual – (object address or name) PID algorithm is stopped when this object value is 1
- output – (object address or name, can be a table with multiple objects) output object (1 byte scaled)
- inverted – (boolean, defaults to false) invert algorithm, can be used for cooling
- min – (number, defaults to 0) minimum output value
- max – (number, defaults to 100) maximum output value
- kp – (number, defaults to 1) proportional gain
- ki – (number, defaults to 1) integral gain
- kd – (number, defaults to 1) derivative gain
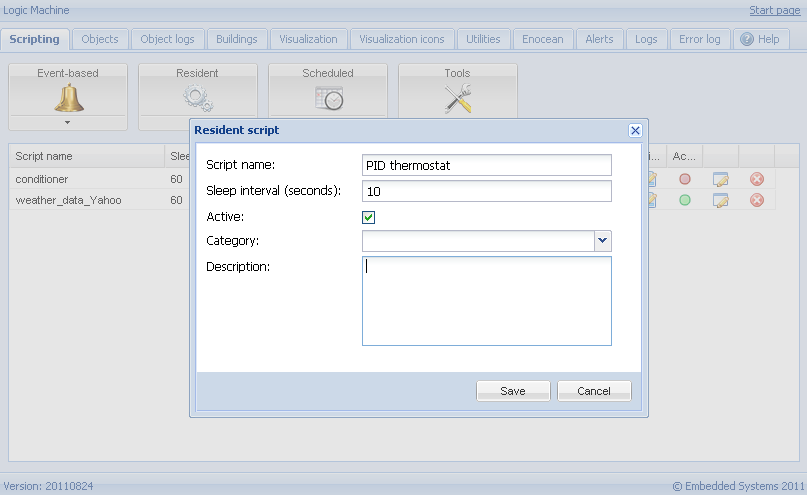
Adding Residential script
PID algorithm should be placed inside a Scripts -> Resident –> Add new script.
Script example:
- -- init pid algorithm
- if not p then
- p = PID:init({
- current = '1/1/1',
- setpoint = '1/1/2',
- output = '1/1/3'
- })
- end
-
- -- run algorithm
- p:run()
Script example with multiple output objects:
- -- init pid algorithm
- if not p then
- p = PID:init({
- current = '1/1/1',
- setpoint = '1/1/2',
- output = { 'PWM 1', 'PWM 2', '1/1/5' }
- })
- end
-
- -- run algorithm
- p:run()
Output value:
p:run() returns output value. If output parameter is not set, you can use the return value to control output objects manually in the script.
Maximum count of PID per device
LogicMachine normally can handle up to 30 PID loops. But it depends on resident script sleep time. We suggest to use a single script for all PID controllers instead of a separate script for each.


